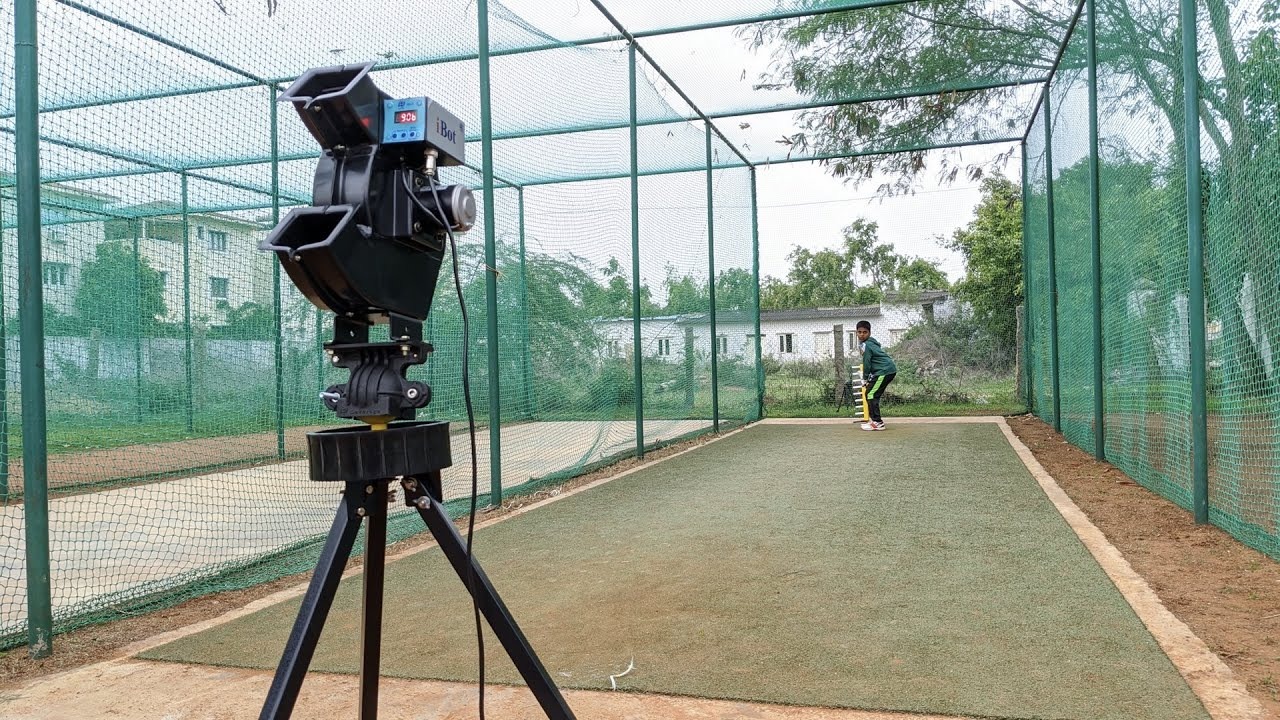
The Ultimate Cricket Bowling Machine Buying Guide (2025)
Introduction
A Cricket Bowling Machine is more than hardware: it’s a training system that amplifies coaching hours and converts repetition into durable motor patterns. For coaches, academy directors, and parents alike, a well-chosen machine reduces variability, increases measurable practice volume, and enables targeted skill acquisition. From an NLP (natural language processing) perspective, used as a metaphor, think of your batting technique as a high-performing language model: to fine-tune it you need large, consistent batches of high-quality input; a bowling machine is the dataset generator.
This guide reframes buying decisions as a signal-to-noise optimization problem: match the machine’s feature vector (speed range, ball compatibility, programmability, portability, durability, support) to the user persona embedding (backyard parent, club coach, academy manager, or mobile coach).
Why Use a Bowling Machine?
A cricket bowling machine is more than a convenience tool — it’s a precision training partner that helps players develop consistency, timing, and shot selection with measurable improvement. Whether you’re a professional coach, an academy instructor, or a home-practice enthusiast, the advantages are clear.
Key Benefits
1. Consistency (High Precision):
Bowling machines deliver balls with the same line, length, and speed repeatedly, enabling batsmen to fine-tune their technique with pinpoint accuracy and eliminate guesswork from training.
2. Focused Drills (Targeted Fine-Tuning):
They allow coaches to isolate specific batting skills — such as the front-foot drive, pull shot, or defensive technique — and repeat them until muscle memory and confidence are built.
3. Speed & Spin Control (Parameter Tuning):
Modern machines offer fully adjustable speed, swing, and spin settings. Coaches can gradually increase the difficulty, helping players adapt to real match conditions with controlled progression.
4. Efficiency (Data Throughput):
A single session with a bowling machine can deliver hundreds of precise deliveries in a fraction of the time needed for traditional net practice, maximizing productivity and feedback opportunities.
5. Programmability & Randomness (Simulation & Augmentation):
Advanced programmable models introduce variation and unpredictability into sessions, simulating match scenarios. Randomized deliveries help players sharpen reflexes, shot selection, and adaptability.
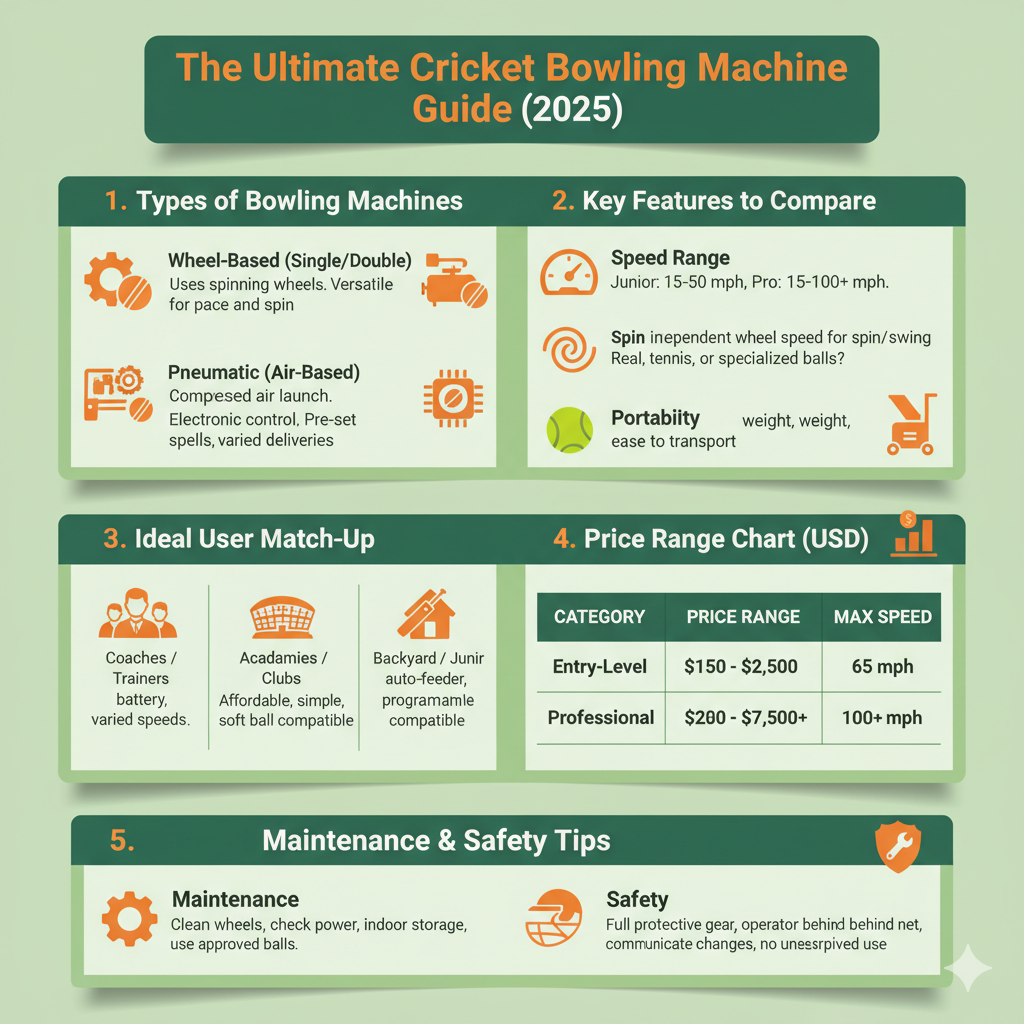
Types of Cricket Bowling Machines — Which One Fits You?
Below are the common delivery systems and the real users they suit. Think of each machine as a model architecture: different inductive biases produce different outcomes.
Two-wheel / Three-wheel rotary machines
How they work: Motor-driven wheels spin and ‘pinch’ the ball between them to project it. Differing wheel speeds, camber, and alignment create pace, seam, and spin.
Who they’re for: Clubs and coaches who need a balance of speed and spin simulation with good reliability and serviceability.
Pros/Cons: Good speed range and spin control; wheel maintenance required; very common in coaching environments.
Arm-action (mechanical arm) machines
How they work: A powered arm mimics a bowler’s swing and release, producing a release plane and oscillation closer to a human bowler.
Who they’re for: Coaches who prioritize the most realistic human-like trajectory and release.
Pros/Cons: Higher realism; often heavier and more mechanically complex; good for seam and swing practice.
Air-cannon / pneumatic machines
How they work: Compressed air propels the ball at very high speeds.
Who they’re for: Raw pace drills, where velocity and impact force are the primary objective, with less emphasis on fine spin control.
Pros/Cons: Very high speeds achievable; less precise spin; often bulky.
Programmable/digital machines
How they work: Electronic controls allow preset sequences, randomization, intervals, and chaining drills.
Who they’re for: Professional academies and high-level coaches who want match-simulation and automation.
Pros/Cons: Excellent for scenario-based training; costlier; requires software control and occasional firmware updates.
Manual/junior / toy machines
How they work: Spring or low-power systems for soft/tennis balls.
Who they’re for: Parents and juniors — safe, cheap, and easy to use.
Pros/Cons: Affordable and simple; limited speed and realism.
Key Features to Compare — What Really Matters
Score each model across them.
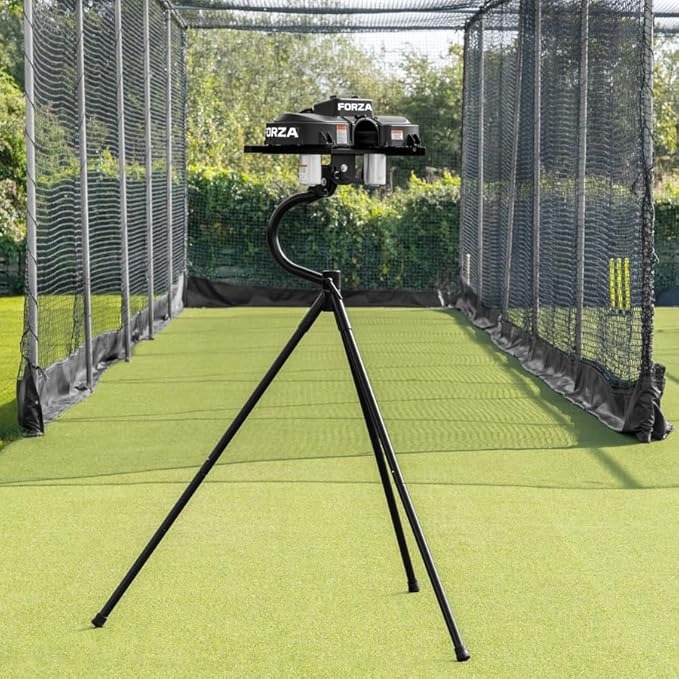

- Speed range (kph/mph): Align this to player level. Many coaching machines span ~60–140 kph; professional models may exceed this speed. Make sure digital readouts or calibration curves are provided.
- Cricket Bowling Machine Buying Guide: http://bit.ly/3IFlYIb
- Spin & swing capability: Can the machine impart top/backspin, side-spin, or emulate a swing? Arm and multi-wheel machines differ substantially.
- Ball compatibility: Leather vs tennis/soft balls — confirm at what speeds leather is safe for the machine and ball life.
- Programmability: Presets, random modes, intervals, repeat counts — crucial for academies and simulation.
- Portability & power: Battery vs mains, chassis weight, foldability, wheels.
- Durability & weatherproofing: Sealed motors and rugged frames for outdoor academy use.
- Warranty & support: Local service reduces downtime — value often exceeds initial purchase price.
- User interface & ergonomics: ePaper displays, tactile buttons, remote control, or app-based control matter for field usability.
- Safety features: Emergency stop, guarding, feed chutes, and shields.
Buyer Personas + Use-Case Matrix
Map user needs (persona embedding) to machine archetypes.
| Persona | Best Type | Minimum Features | Typical Price (USD) |
| Backyard beginner/parent | Junior/manual or low-speed two-wheel | Tennis-ball compatible, lightweight | <$500 |
| Weekend club coach | Two/three-wheel or arm-action | Leather compatible, 60–130 kph, robust wheels | $1,000–$3,000 |
| Professional academy | Programmable high-end (BOLA / Pro) | Wide speed range, spin/swing, service plan | $3,000+ |
| Travel/field coach | Portable battery two-wheel | Easy setup, battery backup, presets | $1,200–$2,500 |
Price bands reflect 2024–2025 retail listings; final costs vary by region, taxes, and dealer configuration.
Top Cricket Bowling Machines for 2025 — Shortlist & What They Do Best
Below are brand and model highlights with the practical reasons to choose each.
BOLA Professional (2025 series) — Best for high-level academies
Why choose it: 2025 control panel upgrades (ePaper), brushless motors, wide speed range, and electronic randomization. Built for heavy-duty, programmable sessions.
JUGS BP2 — Best for versatile coaching
Why choose it: Six preset deliveries (Inswing, Outswing, Off Break, Leg Break, Rising, Low), realistic delivery plane, robust mid-range pricing.
Crick Attack / Sports Attack — Leather-compatible specialist
Why choose it: Designed to accept leather balls, three-wheel configurations enabling seam movement.
Portable two-wheel models — Travel & backyard options
Why choose them: Lightweight, battery operation, quick setup.
Entry-level junior machines / manual throwers — Kids & beginner practice
Why choose them: Low cost, safe, good for early-stage motor learning.
Comparison Table — Specs, Use Cases & Approx Price
| Model / Type | Speed Range | Ball Type | Programmable | Portability | Typical Price (USD) | Best For |
| BOLA Professional (Pro 2025) | 24–152 kph (15–95 mph) | Leather & tennis | Yes — ePaper control & random | Mains / optional battery; moderate | $3k–$8k | Pro academies, clubs |
| JUGS BP2 | ~72–150 kph (40–90 mph) | Leather & tennis | Limited presets (6) | Portable (wheels) | $3k–$3.5k | Coaches, clubs |
| Crick Attack | Varies | Leather & synthetic | Varies | Heavy/durable | $1.5k–$5k | Clubs wanting leather |
| Portable two-wheel | 30–120 kph | Tennis / soft / some leather | Usually limited | Highly portable; battery | $300–$1.2k | Backyard, travel coach |
| Junior/manual | Low speed | Soft/tennis ball | No | Very portable | <$500 | Kids & beginners |
Note: Prices are bands observed in 2024–2025 listings; verify with local dealers.
How a Bowling Machine Works — Simple Tech Explained
At a high level, delivery systems fall into three categories:
- Rotary wheel systems (two/three-wheel): Motor-driven wheels spin and ‘pinch’ the ball forward. RPM differentials adjust pace and side/axis spin.
- Mechanical arm systems: A powered arm swings and releases the ball, closer to a human release plane.
- Pneumatic systems (air cannons): Compressed air ejects the ball at high speed; less precise for spin.
Programmable models coordinate wheel RPMs, actuators, and solenoids to produce repeatable sequences. Session timers, ball counters, and random increments let coaches shape workload and match-like variability.
Feature Deep Dive
Speed & Control
Match speed range to training goals. Look for digital speed readouts or manufacturer-provided calibration charts from RPM to kph. Repeatability is critical: +/- tolerance in speed affects training transfer.
Spin & Swing Simulation
Two/three-wheel and arm machines vary in their ability to generate spin or swing. For seam and late movement, prioritize wheel-angle adjustability and mechanical arm geometry.
Ball Compatibility
Leather compatibility is crucial for match-like practice. Using unsuitable balls increases wear and mechanical risk.
Build & Serviceability
Rugged frames, accessible wear parts (belts, bearings), and clear service documentation reduce downtime. For academies, consider extended support packages and spare parts availability.
Safety Features
Look for guards, emergency stops, wheel covers, and secure feeding chutes. Manufacturer manuals will list required PPE and operating distances.
Maintenance, Safety & Setup Checklist
Follow manufacturer guidance. Quick checklist:
Daily checks
- Inspect delivery wheels/discs for wear.
- Check belts, bearings, and guarding.
- Verify power cables and connectors.
Service schedule
- Annual bearing and motor inspection (or per manufacturer).
- Replace worn delivery wheels per usage cycles.
Ball handling
- Use high-quality leather and retire damaged balls.
- Rotate balls to even wear.
Safety netting & PPE
- Use a safety cage for leather sessions.
- Staff operating the unit should use eye protection and maintain clear communication.
Storage
- Keep electronics dry and protected from dust and moisture.
Pros & Cons — Quick Reality Check
Pros
- Rapid skill acquisition via repetition.
- Better practice efficiency (solo or small groups).
- Programmability for match-like training.
Cons
- High upfront cost for pro units.
- Maintenance and spare parts expenses.
- Some machines can’t fully replicate human variability.
- Leather ball use increases wear and requires strict safety protocols.
Check out this Cricket Bowling Machine Buying Guide (2025) — simple, visual, and smart!
How to Choose — Step-by-Step Decision Flow
- Define use case: Backyard, club, academy, or mobile coach?
- Set a budget: Hobby (<$1k), coach/club ($1k–$3k), pro ($3k+).
- Decide ball type: Will you use leather?
- Portability vs features: Portable battery two-wheel vs heavy programmable pro.
- Local support: Prefer brands with local dealers and spare parts.
Detailed Buying Checklist
- Intended users & practice frequency
- Required ball type (leather vs tennis)
- Speed range required (kph/mph)
- Spin/swing needs (yes/no)
- Programmability needs (presets, random mode)
- Power options (battery + mains)
- Weight & portability
- Warranty & local service availability
- Replacement parts availability (wheels, belts, motors)
- Safety features (guards, e-stop, feed chute)
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Buying the most expensive machine, assuming it’s always best — match features to needs.
- Ignoring service plans and spare parts availability.
- Failing to verify battery runtime for portable units.
- Overlooking user interface ergonomics (hard-to-use controls reduce practical session time).
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can a bowling machine simulate spin and swing?
A: Many modern two/three-wheel and arm-action machines can simulate topspin, backspin, and side-spin.
Q2: What’s the best machine for kids?
A: Lightweight junior/manual machines or low-speed two-wheel models (tennis/softball compatible) are safest for children and beginners.
Q3: How much should I expect to pay?
A: Typical bands: hobby (<$1,000), coach/club ($1,000–$3,000), pro/academy ($3,000+). Prices vary by brand, region, and configuration.
Sample 30-Day Practice Plan Using a Bowling Machine
1st Week — Fundamentals (Days 1–7)
- Daily: 30–40 deliveries at slow–moderate speeds, focusing on straight front-foot drives and leaving.
- Session structure: 5-minute warm-up, 25 minutes focused reps, 5-minute cool-down.
- Goal: Rehearse backlift, timing, and forward stride consistency.
2nd Week — Footwork & Rotation (Days 8–14)
- Intervals: Blocks of 20 deliveries at variable lengths; practice back-foot play and pull shots.
3rd Week — Spin Practice (Days 15–21)
- Use spin settings or wheel differential to practice against off-spin and leg-spin.
- Blocks of 30–40 balls focusing on defensive technique, reading seam, and soft hands.
4th Week — Match Simulation (Days 22–30)
- Randomized sequences and mixed speeds; simulate 6-over spells.
- Pressure drills: Bat with run targets, time limits, and imposed fielding constraints.
Final Verdict & How to Buy
Buying a cricket bowling machine is an investment. Match the persona to features: backyard buyers need portability and Low Cost; clubs need leather compatibility and a mid-range machine; academies benefit from programmable, service-backed pro units. Prioritize durability, spare-part availability, and local support.




